Vectors are important to 3D world, especially Vector3.
Math Basics
Vectors are easy to understand compared to 3D rotations, but not all of them are straightforward. I will extract some important notes about 3D vectors.
Cross Product
- Input: two vectors
- Output: one vector that is perpendicular to other two vectors
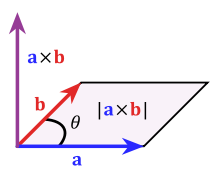
- output vector’s length must satisfy:
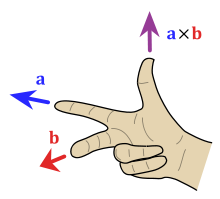
- right-hand rule
derivative process
We know:
Then we can get:
Finally:
Interpolation
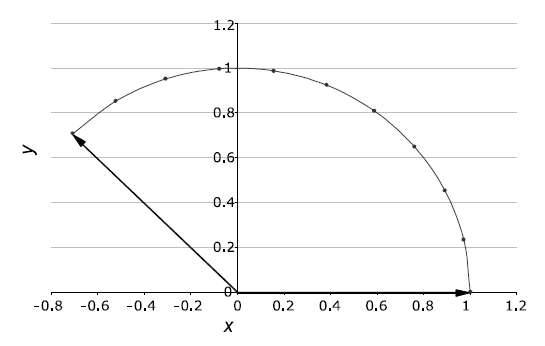
linear interpolation
Linear interpolation can not guarantee the same size of the interpolation vector even when the two input vectors are of the same size. In many applications, we hope that the size of this vector is stable.
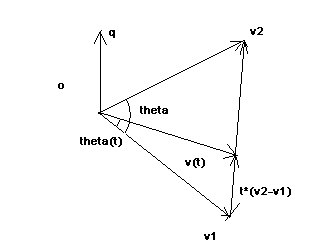
spherical interpolation
The core idea is to add a constraint: the interpolation of two unit vectors must also be a unit vector, which ensures the demand for stable length.
If two vectors are of the same size, the interpolation path is circular; if the vector size is different, the interpolation path is a curve.
The formula is:
My C++ Implementation
Below is an C++ implementation for Vector3, there are other functions/methods which is useful for my work.
// Vector3.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
namespace m3
{
struct Vector3
{
union
{
struct {
float x;
float y;
float z;
};
float v[3];
};
inline Vector3() : x(0.0), y(0.0), z(0.0) {};
inline Vector3(float scalar) : x(scalar), y(scalar), z(scalar) {}
inline Vector3(float x, float y, float z) : x(x), y(y), z(z) {}
bool operator==(const Vector3& v) const;
bool operator!=(const Vector3& v) const;
Vector3 operator+(const Vector3& v) const;
void Add(const Vector3& v);
Vector3 operator+=(const Vector3& v);
Vector3 operator-(const Vector3& v) const;
void Substract(const Vector3& v);
Vector3 operator-=(const Vector3& v);
Vector3 operator*(float s) const;
void Multiply(float s);
Vector3 operator*=(float s);
Vector3 operator/(float s) const;
Vector3 operator/(const Vector3& v) const;
void Divide(float s);
void Divide(const Vector3& v);
Vector3 operator/=(float s);
Vector3 operator/=(const Vector3& v);
float Dot(const Vector3& v) const;
float LenSq() const;
float Len() const;
void Normalize();
Vector3 Normalized() const;
void Clamp(Vector3 min, Vector3 max);
Vector3 Clamped(Vector3 min, Vector3 max) const;
Vector3 Project(const Vector3& v) const;
Vector3 Reject(const Vector3& v) const;
Vector3 Reflect(const Vector3& v) const;
Vector3 Cross(const Vector3& v) const;
static float Angle(const Vector3& v1, const Vector3& v2);
static Vector3 Lerp(const Vector3& start, const Vector3& end, float t);
static Vector3 Slerp(const Vector3& start, const Vector3& end, float t);
static Vector3 Nlerp(const Vector3& start, const Vector3& end, float t);
static Vector3 Min(Vector3 v1, Vector3 v2);
static Vector3 Max(Vector3 v1, Vector3 v2);
static Vector3 Rad2Deg(Vector3 rad);
static Vector3 Deg2Rad(Vector3 deg);
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& output, const Vector3& v);
};
// ---------------------------------------------------------------
Vector3 operator*(float s, const Vector3& v);
Vector3 operator/(float s, const Vector3& v);
}
// Vector3.cpp
#include "Vector3.h"
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
namespace m3 {
#ifndef VECTOR3_EPSILON
#define VECTOR3_EPSILON 0.000001f
#endif // !VECTOR3_EPSILON
#ifndef PI
#define PI 3.14159265358979323846
#endif // !PI
bool Vector3::operator==(const Vector3& v) const
{
return std::abs(x - v.x) < VECTOR3_EPSILON && std::abs(y - v.y) < VECTOR3_EPSILON && std::abs(z - v.z) < VECTOR3_EPSILON;
}
bool Vector3::operator!=(const Vector3& v) const { return !(*this == v); }
Vector3 Vector3::operator+(const Vector3& v) const { return Vector3(x + v.x, y + v.y, z + v.z); }
void Vector3::Add(const Vector3& v)
{
x += v.x;
y += v.y;
z += v.z;
}
Vector3 Vector3::operator+=(const Vector3& v)
{
Add(v);
return *this;
}
Vector3 Vector3::operator-(const Vector3& v) const { return Vector3(x - v.x, y - v.y, z - v.z); }
void Vector3::Substract(const Vector3& v)
{
x -= v.x;
y -= v.y;
z -= v.z;
}
Vector3 Vector3::operator-=(const Vector3& v)
{
Substract(v);
return *this;
}
Vector3 Vector3::operator*(float s) const { return Vector3(x * s, y * s, z * s); }
void Vector3::Multiply(float s)
{
x *= s;
y *= s;
z *= s;
}
Vector3 Vector3::operator*=(float s)
{
Multiply(s);
return *this;
}
Vector3 Vector3::operator/(float s) const { return Vector3(x / s, y / s, z / s); }
Vector3 Vector3::operator/(const Vector3& v) const { return Vector3(x / v.x, y / v.y, z / v.z); }
void Vector3::Divide(float s)
{
x /= s;
y /= s;
z /= s;
}
void Vector3::Divide(const Vector3& v)
{
x /= v.x;
y /= v.y;
z /= v.z;
}
Vector3 Vector3::operator/=(float s)
{
Divide(s);
return *this;
}
Vector3 Vector3::operator/=(const Vector3& v)
{
Divide(v);
return *this;
};
float Vector3::Dot(const Vector3& v) const { return x * v.x + y * v.y + z * v.z; }
float Vector3::LenSq() const { return x * x + y * y + z * z; }
float Vector3::Len() const
{
float lenSq = LenSq();
if (lenSq < VECTOR3_EPSILON) return 0.0f;
return sqrtf(lenSq);
}
void Vector3::Normalize()
{
float lenSq = LenSq();
if (lenSq < VECTOR3_EPSILON) {
return;
}
float invLen = 1.0f / sqrtf(lenSq);
x *= invLen;
y *= invLen;
z *= invLen;
}
Vector3 Vector3::Normalized() const
{
float lenSq = x * x + y * y + z * z;
if (lenSq < VECTOR3_EPSILON) return *this;
float invLen = 1.0f / sqrtf(lenSq);
return (*this) * invLen;
}
void Vector3::Clamp(Vector3 min, Vector3 max)
{
x = std::clamp(x, min.x, max.x);
y = std::clamp(y, min.y, max.y);
z = std::clamp(z, min.z, max.z);
}
Vector3 Vector3::Clamped(Vector3 min, Vector3 max) const
{
return Vector3(
std::clamp(x, min.x, max.x),
std::clamp(y, min.y, max.y),
std::clamp(z, min.z, max.z)
);
}
Vector3 Vector3::Project(const Vector3& v) const
{
float magBSq = v.Len();
if (magBSq < VECTOR3_EPSILON) return Vector3();
float scale = Dot(v) / magBSq;
return v * scale;
}
Vector3 Vector3::Reject(const Vector3& v) const
{
Vector3 projection = Project(v);
return *this - projection;
}
Vector3 Vector3::Reflect(const Vector3& v) const
{
float magBSq = v.Len();
if (magBSq < VECTOR3_EPSILON) return Vector3();
float scale = Dot(v) / magBSq;
Vector3 proj2 = v * (scale * 2);
return *this - proj2;
}
Vector3 Vector3::Cross(const Vector3& v) const
{
return Vector3(
y * v.z - z * v.y,
z * v.x - x * v.z,
x * v.y - y * v.x
);
}
float Vector3::Angle(const Vector3& v1, const Vector3& v2)
{
float sqMagL = v1.LenSq();
float sqMagR = v2.LenSq();
if (sqMagL < VECTOR3_EPSILON || sqMagR < VECTOR3_EPSILON) return 0.0f;
float len = sqrtf(sqMagL) * sqrtf(sqMagR);
return acosf(v1.Dot(v2) / len);
}
Vector3 Vector3::Lerp(const Vector3& start, const Vector3& end, float t)
{
return Vector3(
start.x + (end.x - start.x) * t,
start.y + (end.y - start.y) * t,
start.z + (end.z - start.z) * t
);
}
Vector3 Vector3::Slerp(const Vector3& start, const Vector3& end, float t)
{
if (t < 0.01f) return Lerp(start, end, t);
Vector3 from = start.Normalized();
Vector3 to = end.Normalized();
float theta = Angle(from, to);
float sin_theta = sinf(theta);
float a = sinf((1.0f - t) * theta) / sin_theta;
float b = sinf(t * theta) / sin_theta;
return from * a + to * b;
}
Vector3 Vector3::Nlerp(const Vector3& start, const Vector3& end, float t)
{
Vector3 linear(
start.x + (end.x - start.x) * t,
start.y + (end.y - start.y) * t,
start.z + (end.z - start.z) * t
);
return linear.Normalized();
}
Vector3 Vector3::Min(Vector3 v1, Vector3 v2) { return Vector3(fmin(v1.x, v2.x), fmin(v1.y, v2.y), fmin(v1.z, v2.z)); }
Vector3 Vector3::Max(Vector3 v1, Vector3 v2) { return Vector3(fmax(v1.x, v2.x), fmax(v1.y, v2.y), fmax(v1.z, v2.z)); }
Vector3 Rad2Deg(Vector3 rad) { return rad * 180 / PI; }
Vector3 Deg2Rad(Vector3 deg) { return deg * PI / 180; }
// ---------------------------------------------------------------
Vector3 operator*(float s, const Vector3& v) { return Vector3(v.x * s, v.y * s, v.z * s); }
Vector3 operator/(float s, const Vector3& v) { return Vector3(s / v.x, s / v.y, s / v.z); }
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& output,
const Vector3& v)
{
output << "Vector3(" << v.x << "," << v.y << "," << v.z << ")";
return output;
}
}
References
- Vector Calculus: Understanding the Dot Product
- Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross Product
- 《Rotation Transforms for Computer Graphics》by John Vince
- 《Hands-On C++ Game Animation Programming》by Gabor Szauer